In Part 1 of this 3-part blog on Artificial Intelligence, we discussed “What is Deep Learning“, its key components, the applications of Deep Learning and the future of Deep Learning.
In Part 2 of this 3-part blog, we discussed “What is Machine Learning” the applications of Machine Learning and the future of Machine Learning. As discussed in previous blogs Deep Learning and Machine Learning are both subsets of Artificial Intelligence.
In Part 3 of this 3-part blog, we will talk about Artificial Intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in the 21st century, revolutionizing industries, reshaping economies, and redefining human capabilities. With its ability to simulate human intelligence, AI systems are capable of performing complex tasks, learning from data, and making decisions with minimal human intervention. From self-driving cars to personalized recommendations, AI has permeated various aspects of our lives and holds tremendous potential for the future. In this blog, we will explore the remarkable advancements in AI, its applications across diverse fields, and the impact it is creating in our society.
The below shows Artificial Intelligence and its subsets.
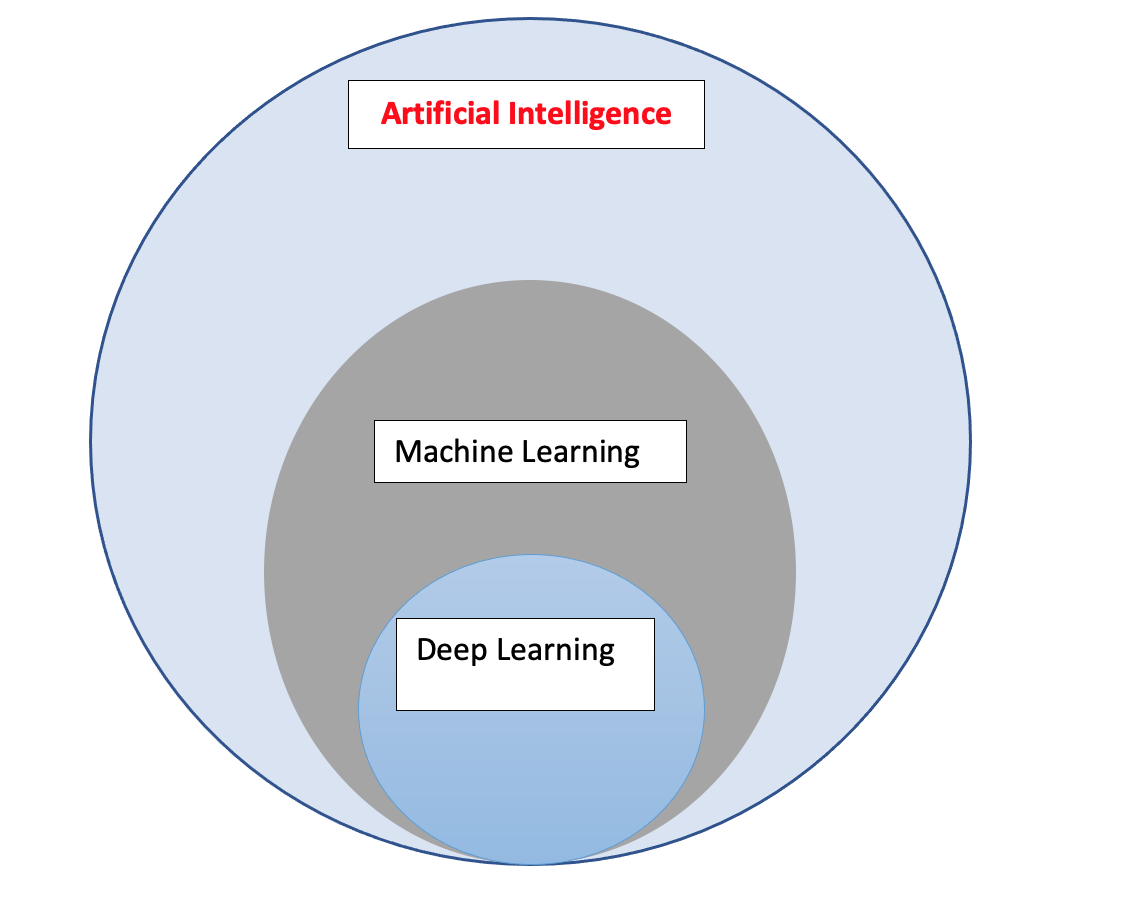

Part 3
Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence: Transforming the Future of Technology and Society
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, one technology is poised to revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us: Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI has gained tremendous momentum in recent years, captivating the imagination of researchers, innovators, and businesses alike. From self-driving cars to voice assistants and personalized recommendations, AI is already reshaping various aspects of our lives.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), once limited to the realm of science fiction, has now become an integral part of our daily routines, transforming industries, enhancing productivity, and driving innovation. AI is a rapidly growing field that aims to develop intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing images and speech, making decisions, and learning from experience. AI has the potential to revolutionize many industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of AI, exploring its applications, potential benefits, the impact it has on society, and ethical considerations.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
While the concept of AI has been around for decades, recent breakthroughs in computing power, data availability, and algorithmic advancements have propelled the field to new heights. AI can be broadly classified into two categories: Narrow AI and General AI. Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, focuses on specific tasks and is prevalent in applications like voice assistants, image recognition, and recommendation systems. On the other hand, General AI, often referred to as strong AI or artificial general intelligence (AGI), aims to possess human-level intelligence and perform any intellectual task that a human can do. The goal of AI is to create machines that can reason, perceive, learn, and adapt to new situations. AI is achieved by creating algorithms that can process data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on that data.
Artificial Intelligence refers to the development of intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as perception, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. These systems are designed to learn from experience, adapt to new inputs, and carry out complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are two prominent branches of AI that have contributed significantly to its recent progress. AI encompasses a wide range of technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more. AI systems are designed to analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, make predictions, and learn from experiences, enabling them to perform complex tasks efficiently and accurately so that they respond to information in ways that mimic human cognitive abilities.
Types of AI systems
AI systems can be classified into different types based on their capabilities and functionality. AI systems often combine multiple techniques and algorithms to achieve the desired functionality. AI is a diverse and rapidly evolving field, and new types of AI systems continue to emerge as research and development progress. The classification of AI systems can also overlap, as many systems incorporate multiple techniques and approaches to solve complex problems. Here are some common types of AI systems:
1. Expert Systems
Expert systems are AI systems that mimic the decision-making capabilities of human experts in specific domains. They utilize knowledge-based rules and algorithms to solve complex problems and provide expert-level advice or recommendations. They use knowledge bases and rules to provide expert-level advice and solutions. Expert systems are often used in fields like medicine, finance, and engineering, where domain-specific expertise is crucial.
They are built using a knowledge base of rules and a reasoning engine that applies those rules to provide expert-level advice or solutions. They use a knowledge base, rules, and inference engines to provide expert-level advice or solve complex problems in areas such as medicine, finance, or engineering.
2. Neural Networks
Neural networks are a type of AI system inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes, or artificial neurons, organized into layers. Neural networks are trained on large datasets to learn patterns and relationships, enabling them to perform tasks such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, predictive analytics, and speech synthesis. They consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers and are trained on large datasets to recognize patterns, classify data, and make predictions.
3. Genetic Algorithms
Genetic algorithms are computational techniques inspired by the principles of natural evolution. They use a population of potential solutions that undergo genetic operations like mutation and crossover to iteratively improve and optimize a problem. They use iterative processes to optimize solutions based on the concept of survival of the fittest. Genetic algorithms are often used in optimization problems, such as finding the best parameters for a given AI model. They are commonly used for optimization problems, search algorithms, and machine learning tasks.
Genetic algorithms are AI systems that use the principles of natural selection and genetic inheritance to solve optimization and search problems. They involve creating a population of potential solutions and iteratively evolving and selecting the best solutions over generations to reach an optimal or near-optimal outcome. Genetic algorithms are used in areas such as engineering design, scheduling, and resource allocation.
4. Fuzzy Logic Systems
Fuzzy logic systems use fuzzy sets and fuzzy reasoning to handle uncertainty and approximate human reasoning. Fuzzy logic systems handle uncertainty and imprecision by allowing for degrees of truth. Unlike traditional binary logic, fuzzy logic systems can handle variables that are partially true or partially false. They are particularly useful in applications where precise, binary decisions are not appropriate, such as in control systems or decision-making processes involving subjective criteria.
Fuzzy logic systems are AI systems that deal with uncertainty and imprecise information. Unlike traditional binary logic, which relies on true/false values, fuzzy logic allows for degrees of truth or membership in a range of values. They are useful in situations where precise or crisp decisions are not possible, such as in controlling systems with imprecise input. Fuzzy logic systems are used in areas such as control systems, decision-making, and pattern recognition where imprecise or incomplete data is present.
5. Reinforcement Learning Systems
Reinforcement learning systems are AI systems that learn from interactions with an environment. They use a trial-and-error approach, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties for their actions, enabling them to learn and improve their decision-making over time. Reinforcement learning systems are capable of learning optimal strategies and have been successfully applied in areas such as game-playing, robotics, and autonomous systems.
6. Natural Language Processing Systems
Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP systems utilize techniques such as text analysis, sentiment analysis, language translation, and chatbots to process and generate natural language. These systems enable computers to process and respond to spoken or written language. They are used in applications such as virtual assistants, customer support, and language translation services. They involve techniques for language understanding, sentiment analysis, machine translation, chatbots, and voice recognition.
7. Computer Vision Systems
Computer vision systems enable computers to interpret and understand visual information from images or videos. These systems can recognize objects, detect patterns, and extract meaningful information from visual data. Computer vision systems find applications in areas such as autonomous vehicles, surveillance, and augmented reality.
8. Planning and Scheduling Systems
Planning and scheduling systems are designed to generate optimal plans or schedules for complex tasks. These systems analyze various factors, constraints, and goals to generate efficient action plans. Planning and scheduling systems are used in logistics, resource allocation, and project management
9. Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Robotics and autonomous systems combine hardware and software to enable machines to perceive and interact with the physical world autonomously. Robotics and autonomous systems involve physical machines or robots that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions without human intervention. These AI systems combine sensors, actuators, and AI algorithms to interact with the physical world. They encompass areas such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, drones, and robotic assistants.
10. Machine Learning Systems
Machine Learning (ML) systems encompass a broad range of AI systems that can learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed. ML systems include various algorithms such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. They are used in diverse applications like predictive modelling, anomaly detection, and data classification. ML systems use algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data, improve performance, and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming.
11. Intelligent Agents
Intelligent agents are software entities that perceive their environment, reason, and take actions to achieve specific goals. They can operate autonomously, adapt to changes, and interact with humans or other systems. Intelligent agents are used in areas such as virtual personal assistants, gaming, and customer service.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI has permeated almost every aspect of our lives, revolutionizing industries and offering new opportunities for innovation. Here are some notable applications of AI:
1. Healthcare
AI is transforming healthcare by enabling early disease detection, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and more accurate diagnoses. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical records, genetic data, and other patient information to identify patterns and make predictions, leading to improved treatment plans and better patient outcomes. ML algorithms can analyze large volumes of medical data, identify patterns, and provide accurate predictions, enabling early detection of diseases and improving patient outcomes.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars are one of the most exciting applications of AI in the transportation industry. By leveraging sensors, computer vision, and machine learning algorithms, autonomous vehicles can navigate roads, make real-time decisions, and enhance road safety. AI also plays a crucial role in optimizing logistics and route planning, leading to more efficient transportation systems.
The advent of self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles is a result of AI advancements. These vehicles use computer vision, machine learning, and sensor technologies to navigate roads, interpret traffic signs, and make real-time decisions, potentially making transportation safer and more efficient. The automotive industry is rapidly adopting AI for autonomous vehicles, enhancing safety, and optimizing traffic flow. AI algorithms enable vehicles to perceive their surroundings, make real-time decisions, and navigate complex road conditions. Additionally, AI is optimizing traffic flow, logistics, and predictive maintenance in this sector.
3. Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly being used to enhance customer service experiences. These systems can understand and respond to customer inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and offer 24/7 support, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced response times. Virtual Assistants and chatbots powered by AI have transformed customer service interactions. These intelligent systems can understand natural language, answer inquiries, and provide personalized recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and reducing response times. Natural language processing enables these systems to understand and respond to human speech, making interactions seamless and efficient.
4. Financial Services
AI is reshaping the finance industry by streamlining processes, detecting fraud, providing personalized financial advice, algorithmic trading, credit scoring, and risk assessment. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time, identifying patterns, predicting market trends, and making informed investment decisions. AI-powered chatbots also enhance customer service by providing personalized recommendations and answering queries promptly.
Intelligent chatbots and virtual advisors are being employed to provide personalized financial recommendations to customers. Moreover, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify trends and patterns, aiding in making informed investment decisions. AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time enables more efficient and informed decision-making.
5. Education
AI is reshaping education by providing personalized learning experiences, intelligent tutoring systems, and adaptive assessments. It can analyze student data, identify knowledge gaps, and tailor instructional content accordingly, empowering students to learn at their own pace. Intelligent tutoring systems can adapt to students’ individual needs, provide personalized feedback, and track progress, leading to more effective and engaging educational outcomes. Intelligent tutoring systems, adaptive learning platforms, and educational data analytics can enhance student engagement and improve educational outcomes.
6. Retail
AI has transformed the retail industry with its predictive analytics capabilities, enabling personalized product recommendations, inventory management, and demand forecasting. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer support and enhance the overall shopping experience.
7. Manufacturing
AI-driven robotics and automation are revolutionizing manufacturing processes, improving efficiency, and reducing errors. AI-powered systems can monitor and optimize production lines, predict maintenance needs, and enhance quality control. Intelligent robots can perform repetitive and complex tasks with precision, increasing productivity and efficiency. AI-powered systems can also optimize supply chain management, predicting demand and optimizing inventory.
Ethical Considerations
As AI continues to advance, it is crucial to address the ethical considerations associated with its use. Here are some key concerns:
1. Bias and Fairness
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. Biased or incomplete data can lead to discriminatory outcomes and reinforce societal biases. Efforts must be made to ensure fairness and inclusivity in AI algorithms and decision-making processes. Ensuring fairness, accountability, transparency and mitigating biases in AI algorithms is crucial to prevent discrimination and ensure equitable outcomes.
2. Privacy and Security
AI relies on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Safeguarding sensitive personal information and ensuring robust cybersecurity measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of data. Implementing robust safeguards and regulations is essential to protect individuals’ data and maintain public trust. Striking the right balance between data utilization and individual privacy rights is an ongoing challenge.
3. Job Displacement
AI’s ability to automate tasks raises concerns about job displacement and its impact on the workforce. While automation may eliminate some jobs, it also has the potential to create new ones and augment existing roles. Preparing the workforce through reskilling and upskilling programs is crucial to navigating this transition effectively.
4. Accountability and Transparency
AI systems can be complex and opaque, making it challenging to understand how decisions are made. AI systems often operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand the underlying decision-making processes. Ensuring transparency, explainability, and accountability in AI algorithms is vital to building trust and mitigating potential risks.
5. Ethical Decision-Making
As AI systems become more autonomous, they may face ethical dilemmas. Decisions made by AI algorithms must align with societal values, and mechanisms for responsible AI development and deployment need to be established.
6. Collaboration and Ethical Considerations
To fully realize the potential of AI, collaboration between various stakeholders is crucial. Researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders need to work together to establish ethical guidelines, promote transparency, and ensure the responsible development and deployment of AI systems. It is imperative to address biases, privacy concerns, and potential societal impacts to create a future where AI benefits humanity as a whole.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI holds tremendous promise. Advancements in AI research, combined with the availability of vast amounts of data and computing power, are driving progress across various domains. Here are a few potential advancements in the future of artificial intelligence:
1. Improved Personalization
AI has already transformed the way businesses interact with their customers. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can generate personalized recommendations, tailor advertisements, and create customized user experiences. AI will leverage data and advanced algorithms to tailor experiences and services to individual preferences and needs. As AI systems become more adept at understanding human behaviour and preferences, we can expect even more personalized and intuitive interactions across various platforms and applications.
2. Enhanced Decision-Making
AI systems will become more sophisticated in their ability to analyze complex data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions. This will benefit fields such as finance, healthcare, and logistics, where AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, enabling more effective decision-making. AI systems will work in tandem with humans, augmenting their capabilities and assisting in decision-making across various domains
3. Augmented Creativity
While traditionally associated with human creativity, AI has already shown its potential to generate original content. From AI-generated music compositions and artwork to creative writing, AI algorithms are capable of augmenting human creativity and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression.
4. Collaborative AI and Human Interaction
Future AI systems will focus on augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing humans. Collaborative AI models will work alongside humans, leveraging their strengths to improve efficiency and productivity. Natural language processing advancements will enable more natural and context-aware interactions with AI systems, making them more intuitive and user-friendly. By automating routine tasks and providing intelligent insights, AI will empower professionals in various fields to focus on higher-level decision-making, creativity, and innovation.
AI systems will assist humans in complex tasks, offering insights, recommendations, and performing repetitive or dangerous tasks. This collaboration will lead to new opportunities and synergies between humans and machines. Natural language processing capabilities of AI will continue to improve, enabling more seamless and human-like interactions with virtual assistants, chatbots, and translation services. Language barriers will gradually diminish, facilitating global communication.
5. Ethical and Responsible AI
As AI continues to evolve, ethical considerations and responsible practices will play a crucial role. Ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI algorithms and decision-making processes will be essential. Researchers and policymakers will focus on developing frameworks and guidelines to address the ethical challenges associated with AI.
6. AI in Scientific Research
Artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionize scientific research by accelerating discoveries and breakthroughs. AI algorithms can analyze vast scientific literature, identify patterns, and assist researchers in finding connections and insights that may have been missed otherwise. This can significantly speed up the process of scientific discovery across disciplines. From drug discovery and genomics to climate modelling and space exploration, AI algorithms will assist scientists in analyzing complex data, identifying patterns, and accelerating the pace of scientific discoveries.
7. AI for Social Good
AI can be a powerful tool for addressing social and environmental challenges. From climate change and poverty alleviation to healthcare accessibility and disaster response, AI technologies can help develop innovative solutions and optimize resource allocation to tackle global issues.
8. Enhanced Automation
AI will continue to automate mundane and repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more creative and high-value work.
9. Healthcare Breakthroughs
AI-driven innovations could lead to breakthroughs in disease prevention, treatment, and drug discovery, potentially saving millions of lives.
10. Smart Cities
AI can contribute to the development of smart cities, optimizing energy consumption, traffic flow, waste management, and improving the overall quality of urban life
11. Robotics and Automation
AI and robotics will continue to merge, enabling the development of advanced robots that can perform complex tasks in various industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. AI-powered robots have the potential to revolutionize industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. Collaborative robots, known as cobots, can work alongside humans, augmenting their capabilities and improving efficiency. From assembly line tasks to surgical procedures, robots equipped with AI algorithms can perform intricate tasks with precision and accuracy, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative endeavours.
12. Climate Change Mitigation
AI can play a significant role in addressing climate change by optimizing energy usage, predicting natural disasters, and facilitating more sustainable practices in industries like agriculture and transportation. As the world faces pressing environmental challenges, AI can play a vital role in addressing climate change. From optimizing energy consumption to developing predictive models for extreme weather events, AI can provide valuable insights and contribute to sustainable practices. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of climate data, enabling better understanding and decision-making to mitigate the impact of climate change.
13. Exploration and Discovery
AI can assist in scientific research and exploration, aiding in the discovery of new materials, understanding complex phenomena, and expanding our knowledge of the universe.
14. AI and Sustainability
AI will contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource consumption, improving energy efficiency, and enabling better waste management. AI-driven smart grids, precision agriculture, and environmental monitoring systems will help address pressing ecological challenges.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence has the power to reshape our world, offering immense potential for innovation, efficiency, and improved quality of life. Interdisciplinary efforts involving experts from various fields, including computer science, ethics, law, and social sciences, can help shape AI development in a way that aligns with societal values and priorities. Its applications span across numerous industries and have the potential to bring about transformative changes.
However, as we embrace the possibilities of AI, it is crucial to address the ethical considerations associated with its implementation. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems is essential to mitigate potential biases and maintain public trust. It is crucial for organizations and policymakers to establish clear guidelines and regulations regarding the ethical use of AI, including data privacy, security, and responsible decision-making. Furthermore, promoting diversity and inclusivity in AI development and deployment is vital to prevent the reinforcement of societal biases and ensure that AI benefits all individuals and communities equally.
In conclusion, Artificial Intelligence has emerged as a transformative force with the potential to reshape our world. From healthcare and finance to transportation and customer experiences, AI is already making a significant impact across various sectors. As we embrace this technology, it is crucial to prioritize ethical considerations, promote responsible development, and foster collaboration between humans and AI systems. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of AI and create a future where intelligent machines work in harmony with humanity, driving progress and improving the quality of our lives.


